Week2 : DB connection & CRUD
Database connection
- Install the
mysqllibrary to your project, by enter the command linenpm install mysql2
- Import the
mysqllibrary to your project.
const mysql = require("mysql2");
- Add the following code
- This is the
database configurationof your database.
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: "tutorialdb.pspgun.com",
port: "13308",
user: "",
password: "",
database: "csc-105",
});
- Connect to the
database
- This line of code is using the
connectionvariable from above to connect to the database using.connect()method.
connection.connect((err) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
console.log("Database is connected");
}
});The code
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const mysql = require("mysql2");
const port = 3000;
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: "server2.mixkoap.com",
port: "6105",
user: "user",
password: "password",
database: "csc105-workshop",
});
// Connect to database
connection.connect((err) => {
if (err) {
console.log(err);
} else {
console.log("Database is connected");
}
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`);
});
- Restart the applcation
- If your database connection is invalid, it will show you an error. ❌👇🏻
- If your database connection is valid, your application will run correctly. ✅👇🏻
Let's write the endpoint that query todo-list data from the database and response to the user.
- This the schema of
sampledatabase 👇🏻
Example of GET method
- Let's create a first endpont query all todo-list from the database.
- In the path
/todo/all, it will query from all data fromitemstable. - We will use the
.query()method to insert your SQL query. - The second argument to the
.query()method is a callback function(err, rows), which will be called when the MySQL send the response. The callback function takes two arguments,errandrows, which represent theerrorof the database androwsobjects for response data from MySQL database. Ifwe found an error, we will response the error message to the client.else, we will returnrowwhich is data from theitemstable from the database. 👇🏻
app.get("/todo/all", (req, res) => {
connection.query("SELECT * FROM items", (err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
return res.json({
success: true,
data: rows,
error: null,
});
}
});
});
- Let's run your application again, and go to the path
localhost:3000/todo/all
- You will see the data that response to the client.
- Let's install a program that you can test your API easier!
- Go to download and install the Postman via https://www.postman.com/downloads/
Postman is an API platform for building and using APIs. Postman simplifies each step of the API lifecycle and streamlines collaboration so you can create better APIs—faster.
- Open the Postman
- Click
+ - Click
Add a requestto add a request.
- (1) Name your request
- (2) Enter your request path (localhost == 127.0.0.1)
- (3) Click
Send
- After you clicked send, it will show the response data from your backend application. 👇🏻
- You can use Postman to test your API from your backend application here. that easier than testing on your website. 😊
Let's back to our backend application.
Example of query parameter URL
- Create a endpoint that query a todo-list by
idusingparametersfrom URL.
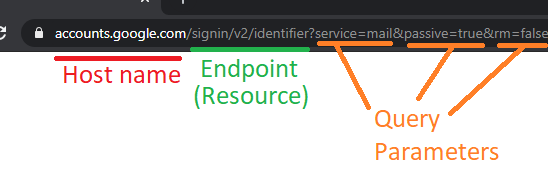

- This is how
query parameterworks in URL 👆🏻 - In this code, we have ...
const todoId = req.query.todo_id;
- that be a
query parameterfor this endpoint.
app.get("/todo", (req, res) => {
// Assign the params as a variable
// https://medium.com/@joseph.pyram/9-parts-of-a-url-that-you-should-know-89fea8e11713
const todoId = req.query.todo_id;
// Regex to check the todo_is is a number only or not
const checkTodoId = new RegExp(/^\d+$/).test(todoId); // Boolean
// Check if the todo_id is not exist or is not a number, return json with an error
if (!todoId || !checkTodoId) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: "todo_id is invalid",
});
}
connection.query(`SELECT * FROM items WHERE id = ${todoId}`, (err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
if (rows[0]) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: rows[0],
error: null,
});
} else {
res.json({
success: true,
data: null,
error: null,
});
}
}
});
});
- Let's try sending a request by creating a new request at Postman
- Create a request.
http://127.0.0.1:3000/todo?todo_id=1
- Click
Send - The response from your backend application 👇🏻
Example of the POST method
- Create an endpoint that create a
user
-
Before writing a request, we need to install the library
body-parserfirst. -
npm i body-parser -
Because Express JS cannot read the JSON body request directly, So we need to install
body-parserfirst.
const bodyParser = require("body-parser"); // import the body-parser
// parse various different custom JSON types as JSON
app.use(bodyParser.json({ type: "application/json" }));
Code ...
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const mysql = require("mysql2");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser"); 👈🏻
const port = 3000;
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: "server2.mixkoap.com",
port: "6103",
user: "root",
password: "root_apisitmaneerat",
database: "csc105-workshop",
});
// Connect to database
connection.connect();
console.log("Database is connected");
// parse various different custom JSON types as JSON
app.use(bodyParser.json({ type: "application/json" })); 👈🏻
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello World!");
});
.
.
.
.
.
.
- Create an endpoint
app.post("/todo/create", (req, res) => {
// The JSON body
const payload = req.body;
connection.query(
`INSERT INTO users (username) VALUES (?)`, [payload.userName], (err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
console.log(rows);
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "create success",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
- The request body mostly send in
JSONformat 👆🏻 - Create a request in Postman and change the HTTP method to
POST
****Remark - HTTP Methods 👇🏻
- Add the
JSONbody 👇🏻
http://127.0.0.1:3000/todo/create
{
"userName" : "Apisit Maneerat"
}
- Click
Send
-
The response from your backend application. 👆🏻
-
In the Database 👇🏻
- For more detail
Example of the PATCH method
- Create an endpoint that edit the data in the Database
- For example we are going to change the
nameanddetailfromid = 1
- Create the endpoint
- For this endpoint we use
.patch()because we are going to edit some fields that you specific in the Database.
app.patch("/todo/edit", (req, res) => {
// The JSON body
const payload = req.body;
console.log(payload);
connection.query(
"UPDATE items SET name = ?, detail = ? WHERE id = ?", [payload.name, payload.detail, payload.id],
(err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "update successfully",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
- Create a request in Postman
- Click
Send
Example of the DELETE method
- Create an endpoint that delete the data from the
linkstable in the database.
- For this endpoint, we will use
.delete()because we are going to delete data from the database. - We use
query stringto get the data from the client - Create an endpoint 👇🏻
app.delete("/todo/delete", (req, res) => {
// Assign the params as a variable
const id = req.query.id;
const todoId = req.query.todo_id;
connection.query(
`DELETE FROM links where id = ? AND todo_id = ?`, [id, todoId],
(err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "delete successfully",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
- Create a request in Postman
- Click
Send
--- End of the example ----
** This is the finalized code for this example 👇🏻
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const mysql = require("mysql2");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const port = 3000;
const connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: "server2.mixkoap.com",
port: "6103",
user: "root",
password: "root_apisitmaneerat",
database: "csc105-workshop",
});
// Connect to database
connection.connect();
console.log("Database is connected");
// parse various different custom JSON types as JSON
app.use(bodyParser.json({ type: "application/json" }));
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello World!");
});
app.get("/hello", (req, res) => {
res.json({
name: "Apisit Maneerat",
nickName: "Mixko",
university: "KMUTT",
});
});
app.get("/todo/all", (req, res) => {
connection.query("SELECT * FROM items", (err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
res.json({
success: true,
data: rows,
error: null,
});
}
});
});
app.get("/todo", (req, res) => {
// Assign the params as a variable
// https://medium.com/@joseph.pyram/9-parts-of-a-url-that-you-should-know-89fea8e11713
const todoId = req.query.todo_id;
// Regex to check the todo_is is a number only or not
const checkTodoId = new RegExp(/^\d+$/).test(todoId); // Boolean
// Check if the todo_id is not exist or is not a number, return json with an error
if (!todoId || !checkTodoId) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: "todo_id is invalid",
});
}
connection.query(`SELECT * FROM items WHERE id = ${todoId}`, (err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: `Data not found ${err.message}`,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
if (rows[0]) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: rows[0],
error: null,
});
} else {
res.json({
success: true,
data: null,
error: null,
});
}
}
});
});
app.post("/todo/create", (req, res) => {
// The JSON body
const payload = req.body;
connection.query(
`INSERT INTO users (username) VALUES (?)`,
[payload.userName],
(err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "create successfully",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
app.patch("/todo/edit", (req, res) => {
// The JSON body
const payload = req.body;
console.log(payload);
connection.query(
"UPDATE items SET name = ?, detail = ? WHERE id = ?",
[payload.name, payload.detail, payload.id],
(err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
// Return data to the client if success
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "update successfully",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
app.delete("/todo/delete", (req, res) => {
// Assign the params as a variable
const id = req.query.id;
const todoId = req.query.todo_id;
connection.query(
`DELETE FROM links where id = ? AND todo_id = ?`,
[id, todoId],
(err, rows) => {
// Check if cannot find the data in the database then return the error
if (err) {
return res.json({
success: false,
data: null,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
if (rows) {
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
message: "delete successfully",
},
});
}
}
}
);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`);
});
More examples for those who want to create more than one query in one endpoint
app.get("/todo/from", async (req, res) => {
const userId = req.query.userId;
// User data
const userData = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
connection.query(
`SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = ?`,
[userId],
(err, rows) => {
if (err) {
res.json({
suceess: false,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
resolve(rows[0]);
}
}
);
});
// User's todos
const userTodos = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
connection.query(
`SELECT * FROM items WHERE owner_id = ?`,
[userId],
(err, rows) => {
if (err) {
res.json({
suceess: false,
error: err.message,
});
} else {
resolve(rows);
}
}
);
});
res.json({
success: true,
data: {
user_data: userData,
todos: userTodos,
},
error: null,
});
});

























